Surface Strengthening and Support
2020
KARABÜK - KARADENİZ - Turkey
REGIONAL DIRECTORATE OF HIGHWAY AUTHORITY OF TURKEY
KARABUK – ESKIPAZAR ROAD PROJECT
Problem
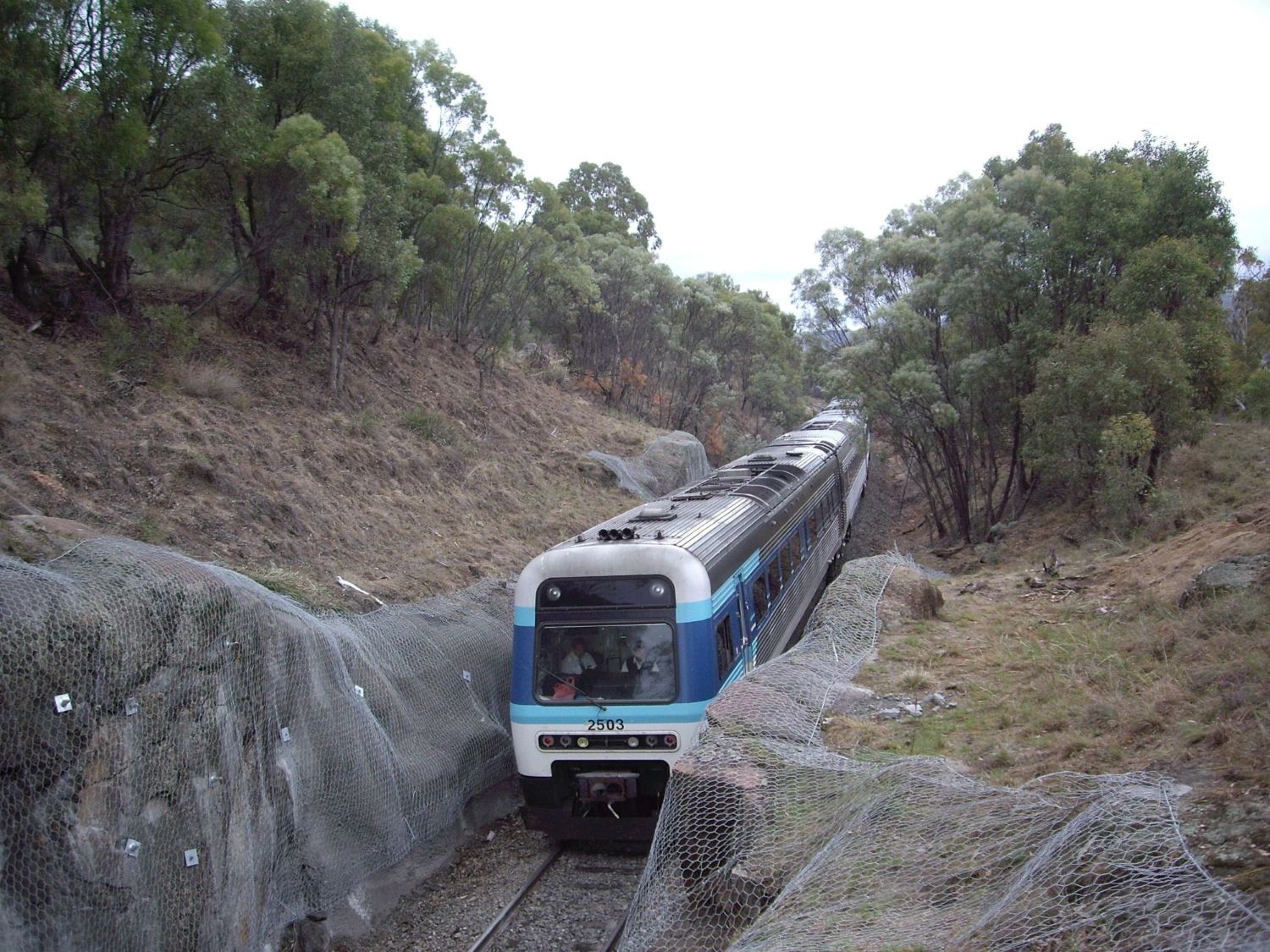
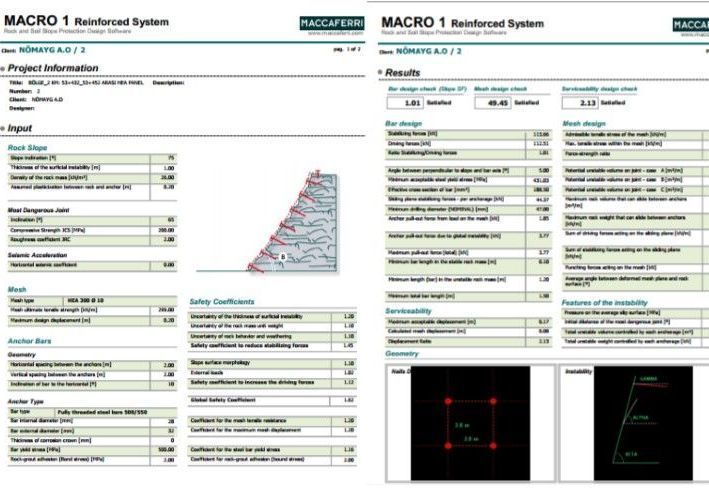
Along the Karabuk – Eskipazar 4 Hd. Road between km: 6+470-6+720 (right) and km: 7+510-7+660 (right), which is under the responsibility of 15th Regional Directorate of Highways, medium and large scale rockfall were observed due to superficial alteration on the slopes consisting of weathered limestone-claystone-marl intercalations. The total area is approximately 20,000 m². Due to the sensitivity of clay and marl levels to water, material losses have been experienced due to the surface water flow on the slope. This has caused the carving of solid limestone layers to hang up. And these blocks were caused to fall in time. The falling materials have caused deformation of the stone Wall. It has fallen on the road by exceeding the Wall, and it has been seen that it effect road safety in the negative direction. In order to protect against these risks mentioned above, on-site inspection were carried out by our technical team, calculations and design were made on the data obtained from the inspection, and appropriate capacitive materials and surface slope protection applications were determined.
Çözüm
According to the calculations made to ensure the consolidation of on-site consolidation of the rock blocks on the small-medium scale with the potential for failure, and to prevent the flow of thin-gauge materials, use of steel wire rope composite wire netting systems (MacMat HS) with a tensile strength of 73 kN/m, equipped with steel ropes at 100 cm intervals and composed of polymeric fibers, with 3mx3m raster and 4m long rock bolt. And it was seen that these bolts had to be manufactured by connecting them with 8 mm thick diagonal ropes. The polymeric fibrous structure of the MacMat HS material is resistant to displacement of the fine material caused by weathering. The steel composite material that is knitted with ropes is resistant to loads that will form by the breakage of the limestone.
Used Products
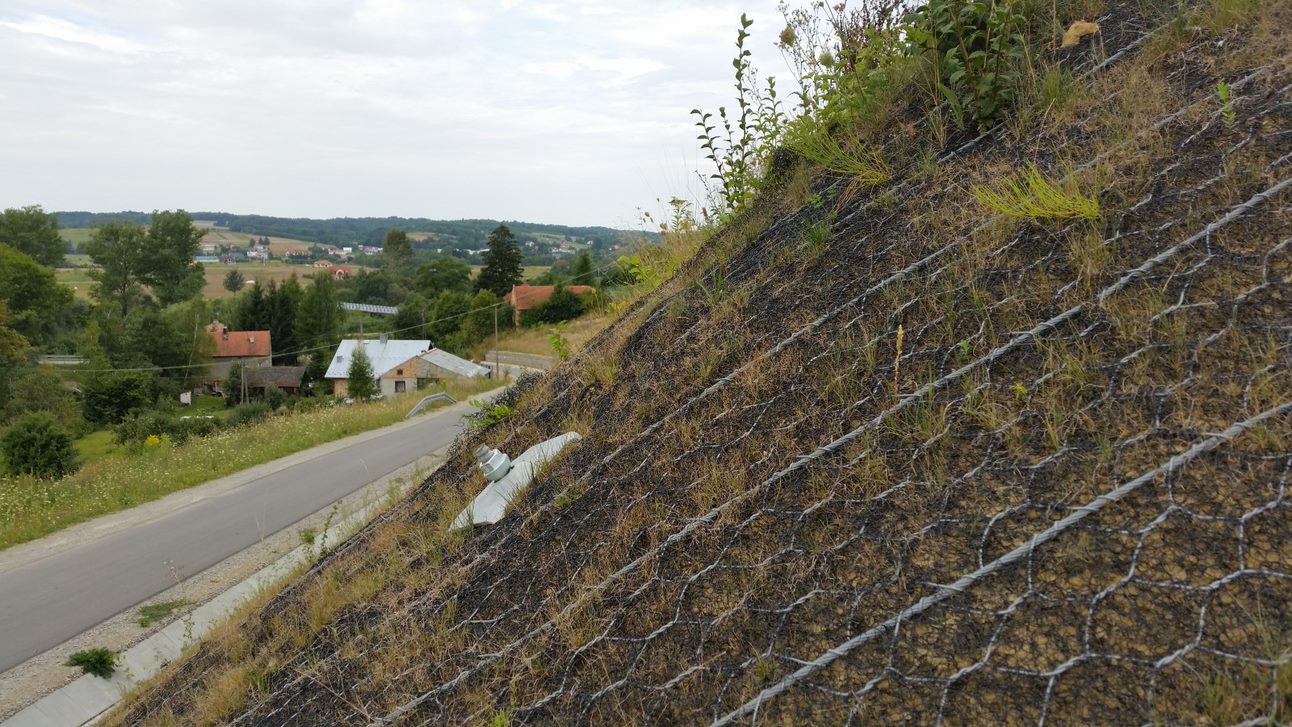

MacMat HS
Macmat® R, ekstrüde üç boyutlu polimer liflerin, çift bükümlü çelik tel ağ donatıları üzerine kompozit olarak imal edilmesi ile elde edilen donatılı gGörüntüle